Interventional pulmonology (IP), an advanced subspecialty of pulmonary medicine, focuses on using minimally invasive procedures and therapeutic techniques to diagnose and treat conditions in the lungs and chest. IP procedures yield exceptional outcomes and offer patients the potential advantage of avoiding more invasive surgery.
Inova's nationally recognized IP program treats more patients than any other program in the Washington, DC metropolitan area. Our team of board-certified interventional pulmonologists work hand-in-hand with an expert team of thoracic surgeons, oncologists, radiation oncologists and respiratory therapists to successfully manage complex airway and pleural diseases, including lung cancer and non-malignant diseases of the chest.
Conditions we diagnose and treat
- Airway obstructions
- Airway malacia (Tracheobronchomalacia or TMB)
- Airway stenosis
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
- Emphysema
- Enlarged lymph nodes
- Foreign body removal from the trachea and airways
- Lung Cancer Screening and Treatment (See Lung Cancer Screening Program and Inova Thoracic Oncology Program)
- Lung nodules
- Lung transplants
- Pleural Effusions (cancerous and non-cancerous)
- Severe asthma
IP procedures we offer
- What is it? Using a bronchoscope, wire mesh stents are placed in narrowed airway tubes and expanded to open the airways and alleviate undesirable symptoms (e.g. difficulty breathing, cough, pneumonia) caused from a constriction.
- Who can benefit? Patients with cancer or another pulmonary condition that constricts or compresses an airway tube.
- What is it? A deflated balloon is placed into a section of an abnormally narrowed airway tube. By inflating the balloon with saline, the airway is expanded to alleviate undesirable symptoms (e.g. difficulty breathing, cough, pneumonia) caused from a constriction. This procedure may be performed prior to airway stent placement to help expand a bronchus.
- Who can benefit? Patients with cancer or another pulmonary condition that constricts or compresses an airway tube.
 What is it? This common IP procedure allows doctors to look at a patient’s lungs and airways. The bronchoscope – a thin, lighted tube – is inserted into the airways through a patient’s mouth or nose. Images from the lungs are displayed on a video screen. Pictures may also be captured.
What is it? This common IP procedure allows doctors to look at a patient’s lungs and airways. The bronchoscope – a thin, lighted tube – is inserted into the airways through a patient’s mouth or nose. Images from the lungs are displayed on a video screen. Pictures may also be captured.
Additionally, the bronchoscope has a channel at its tip, through which a doctor can pass small tools. Using these tools, the doctor can perform several other IP procedures.
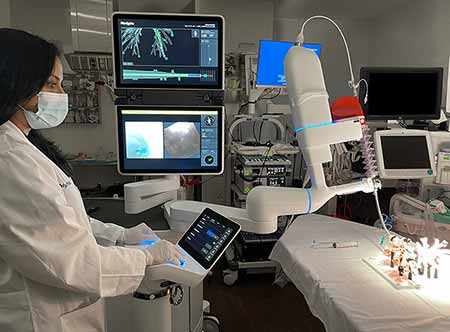
Inova’s robotic-assisted bronchoscopy technology is used to diagnose lung nodules and enhances stability, precision, airway navigation and efficiency. It represents the latest advancement in the fight against lung cancer. With the addition of this new technology, Inova now offers comprehensive robotic, minimally invasive diagnostic and treatment options for lung cancer patients.- Who can benefit? Bronchoscopy can help diagnose abnormalities seen on chest x-rays or CT scans, infection, transplant rejection, the cause of shortness of breath or persistent cough and more.
- What is it? A procedure where saline solution is injected through the bronchoscope into a segment of the lung. The fluid is then suctioned into a sterile container for testing.
- Who can benefit? This procedure can help diagnose infection, cancer, bleeding and other pulmonary conditions.
- What is it? BLVR is a cutting-edge minimally invasive treatment where endobronchial valves – small, one way valves – are placed by flexible bronchoscopy into the airways. The valves reduce lung volumes by allowing secretions and trapped air to escape, while also preventing air from entering that section of the lung. This procedure reduces shortness of breath and makes breathing easier for patients with emphysema/COPD.
Learn More
- Who can benefit? Patients with advanced chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)/emphysema.
- What is it? During the bronchoscopy, the doctor applies a heated probe to the walls of the airways. This destroys the smooth muscle layers that contribute to asthma symptoms.
- Who can benefit? Patients with severe asthma that can’t be controlled with medications.
- What is it? ENB is a diagnostic pulmonary procedure. This advanced system guides the bronchoscope further than a traditional bronchoscopy. Using the patient’s CT scan, the physician is able to biopsy hard-to-reach abnormal areas of the lung that would normally require more invasive testing.
- Who can benefit? ENB can help diagnose a variety of lung disorders, including inflammation, infections and cancer.
- What is it? EBUS is a diagnostic pulmonary procedure. The EBUS scope has a video camera with an ultrasound probe attached to create images of your lungs and lymph nodes. It is inserted through the mouth and into the windpipe and lungs.
- Who can benefit? EBUS can help diagnose a variety of lung disorders, including inflammation, infections and cancer, without invasive surgery.
- What is it? Using imaging guidance, such as fluoroscopy during a bronchoscopy, small metal objects called fiducial markers are placed in or near a tumor in preparation for radiation therapy. The markers help pinpoint the tumor’s location with greater accuracy.
- Who can benefit? Generally, cancer patients receiving radiation therapy (stereotactic radiation surgery or proton therapy) will have fiducial markers placed.
What is it? Bronchoscopy is the preferred IP procedure to remove inhaled foreign objects that are lodged in an airway. A doctor may be able to remove the object using the flexible and/or rigid bronchoscopy.
Who can benefit? Patients with a foreign object lodged in an airway.
- What is it? A diagnostic procedure where tissue or cells are removed from the lung or lymph node for examination.
- Who can benefit? Biopsies help detect cancer, infection, sarcoidosis and other pulmonary conditions.
- What is it? A treatment that uses special drugs (photosensitizing agents) and light from lasers to kill cancer cells.
- Who can benefit? Patients diagnosed with certain types of localized, early stage cancers that have not spread outside of the lungs.
- What is it? A pleuroscope (a type of endoscope) is inserted through a small chest incision into the fluid-filled space that surround the lungs (pleura). This minimally invasive procedure is done under anesthesia and allows the doctor to view of the outside edges of the lung.
- Who can benefit? This procedure can help diagnose pleural (lining of the lung) diseases and conditions, lung cancer and tuberculosis.
- What is it? A catheter is inserted into the chest wall through a needle to drain excess fluid surrounding the lungs. Once drained, the catheter is removed and discarded. The doctor may collect samples of the fluid for further testing.
- Who can benefit? This is a common procedure for patients diagnosed with pleural effusion.
What is it? Varying types of minimally invasive techniques used to shrink or destroy cancerous cells/tumors.
- Radiofrequency ablation: Uses high-energy radio waves to heat and destroy abnormal tissue and cancer cells. This method is often used on large, obstructing tumors in the airway.
- Cryotherapy (cold therapy): Uses extremely cold temperatures from liquid nitrogen or argon gas to destroy abnormal tissue and cancer cells. It can also be used to treat post-surgical scar tissue forming in the airways.
- Laser therapy: Uses intense, narrow beams of light to remove or destroy abnormal tissue and cancer cells. Lasers may also be used to ease certain symptoms of advanced cancer, such as bleeding or blockages.
- Electrocautery: Uses heat from an electrical current to destroy abnormal tissue and cancer cells. It can also stop bleeding from abnormal tissue in the airway.
Who can benefit? Patients diagnosed with certain types of cancer.
- What is it? A pleural catheter is an alternative to pleurodesis for the treatment of recurrent pleural effusion. Through minor surgery, a plastic catheter is tunneled beneath the skin and into the chest cavity. As excess pleural fluid accumulates around the lung, the patient can drain the catheter at home using special sterile supplies.
- Who can benefit? This procedure allows patients to better manage shortness of breath from recurrent malignant pleural effusions safely at home.
What is it? A procedure where saline solution is inserted through a breathing tube into the airways to "flush" or "wash" the lungs. This procedure is performed under anesthesia.
Who can benefit? Patients diagnosed with pulmonary alveolar proteinosis (PAP), caused by a build-up of sand-like material in the air sacs (alveoli) of the lungs.